Describe the Dissolving Process at the Molecular Level
This takes place at the surface of the solute. Describe the process of dissolving.

Solutions And Solubility Ppt Download
Copper plating is the process of plating a layer of copper electrolytically on the surface of an item.

. What occurs at the molecular level to cause a solute to dissolve in a solvent. When a solute dissolves the individual particles of solute become surrounded by solvent particles. The Dissolution Process.
We will first examine the process that occurs when an ionic compound such as table salt sodium chloride dissolves in water. When a soluble solute is introduced into a. To understand this process at the molecular level we must apply the three steps we previously discussed.
The solubility of molecular solids in molecular solvents is again governed by the like dissolves like principle. The concept of dissolving is when a solid called a solute completely mixes with a liquid called a solvent at the molecular level to become a single visible phase and become a homogeneous mixture. Dissolving needs another term to be used this is solvation.
So a solvent film occurs around the molecule in other wordsa solvent-like micro-environment is formed. The polar isopropanol molecules are attracted to the. The following are statements about the dissolving process.
At the molecular level the individual solid molecules become separated and interact less with each other and more with surrounding solvent molecules. In molecular crystals the attractive forces are weak being of the London dispersion dipole-dipole or hydrogen-bonding type. Describe on a molecular level the difference between the two physical changes melting and dissolving Step-by-step solution Chapter 33 Problem 3E is solved.
Dissolving occurs when the solute is pulled apart by the solvent. The copper then physically flows to the item where it is reduced to the metallic state by gaining. Briefly describe the solution process at the molecular level.
Problem 3 Easy Difficulty. Recall the rule that like dissolves like. As we saw in Section 91 Solutions this means that substances must have similar intermolecular forces to form solutions.
An earlier chapter of this text introduced solutions defined as homogeneous mixtures of two or more substancesOften one component of a solution is present at a significantly greater concentration in which case it is called the solventThe other components of the solution present in relatively lesser concentrations are called solutesSugar is a covalent solid composed of. The solute particles must separate form the other solute particles. Up to 24 cash back There are 3 steps to the dissolving process.
The first step in the dissolving process is endothermic. Water typically dissolves many ionic compounds and polar molecules. This process requires energy to overcome forces of attraction between solvent particles.
Dissolving a solid in a liquid depends on the interactions and attractions between the molecules of the liquid solvent and the particles of the solid solute. Table sugar is sucrose C 12 H 22 O 11 and is an example of a molecular compound. Molecular view of the solution process - When solute dissolves in solvent particles of the solute disperse throughout the solvent.
Students use molecular-level models to explain how these sub-microscopic processes affect the macroscopic observable characteristic of the temperature increasing or decreasing during the process of dissolving. This nonstop attack continuous until the whole NaCl crystal disintegrates. Hydration helps to stabilize aqueous solutions by preventing the positive and negative ions from coming back together and forming a precipitate.
Eventually the particle detaches from the remaining solute surrounded by solvent molecules in solution. Increasing the pressure of a solute gas above a liquid solution increases the solubility of the gas in the liquid. Use the dissolution of a solid in a liquid as an example.
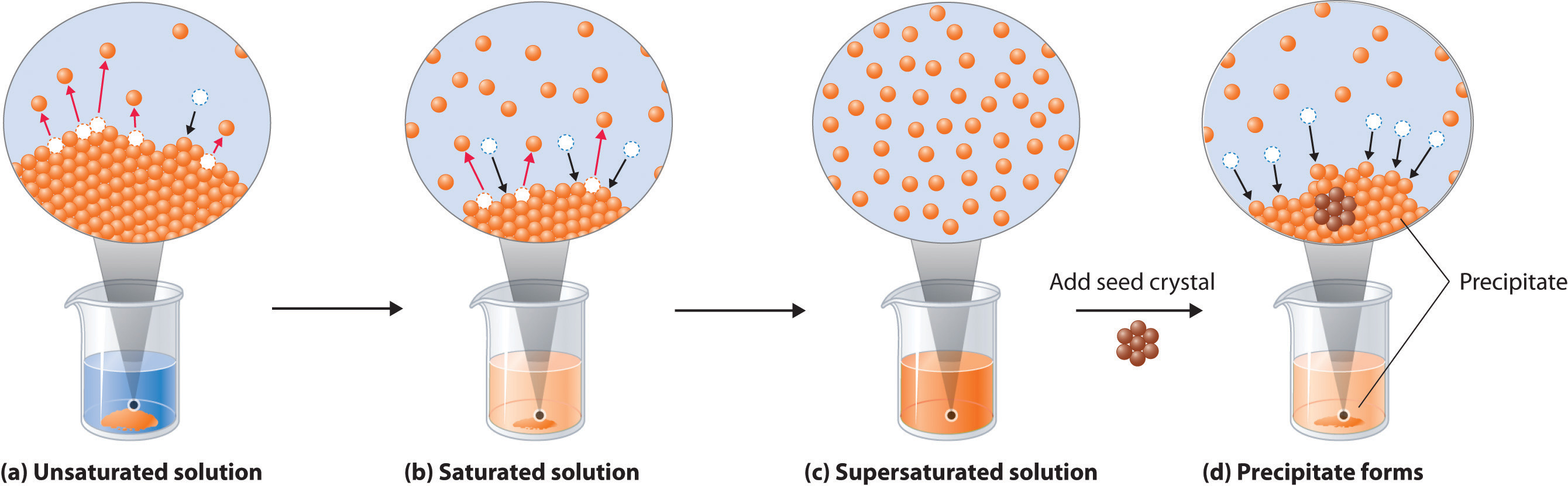
As illustrated in Figure 3 the formation of a solution may be viewed as a stepwise process in which energy is consumed to overcome solute-solute and solvent-solvent attractions endothermic processes and released when solute-solvent attractions are established an exothermic process referred to as solvation. Nonpolar molecules such as those found in grease or oil do not dissolve in water. The answer depends in part on the solute but there are some similarities common to all solutes.
Describe what happens on the molecular level as the water dissolves in the isopropanol. As illustrated in Figure 3 the formation of a solution may be viewed as a stepwise process in which energy is consumed to overcome solute-solute and solvent-solvent attractions endothermic processes and released when solute-solvent attractions are established an exothermic process referred to as solvation. This means that substances must have similar intermolecular forces to form solutions.
The answer depends in part on the solute but there are some similarities common to all solutes. Dissolving happens when the attraction between the particles of the solvent and solute are strong enough to overcome the attraction of the particles of the solute for one another. The dissolving process is how a solution is formed.
Hydration is the process of solute particles being surrounded by water molecules arranged in a specific manner. Recall the rule that like dissolves like. Solute particles occupy position which are normally occupied by solvent molecules.
As the copper ions dissolve into the water they form a coordination complex with salts already present. What occurs at the molecular level to cause a solute to dissolve in a solvent. The solvent particles must move apart to make room for solute particles.
The relative magnitudes of the energy changes. This helps the solvated molecule be soluble in the solvent. Students look at illustrations of these substances on the molecular level.
In molecular nature similar solute molecules are. Increasing the temperature of water speeds up the rate at which many solids dissolve in this solvent. Students see that four different substances salt MSG Epsom Salt and sucrose dissolve to different extents in water.
In the case of molecular solutes like glucose the solute particles are individual molecules. The concept of dissolving is when a solid called a solute completely mixes with a liquid called a solvent at the molecular level to become a single visible phase and become a homogeneous. Solvation is briefly surrounding of solvent molecules around solute molucule.
The relative magnitudes of the energy changes. Explain each one at the molecular level. Students see that the process of dissolving involves the attraction and interaction of the molecules of the liquid and the solid.
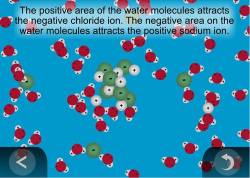
Sodium chloride NaCl dissolves when water molecules continuously attack the NaCl crystal pulling away the individual sodium Na and chloride Cl ions.

4 1c Solution Chemistry Describe The Dissolving Process Cset Study Guide Chemistry

Use This Lessonplan When Teaching Why Water Dissolves Sugar In Your Middleschool Science Classroom Middle School Chemistry Science Method Science Lessons

Research Reveals How An Acid Dissolves Molecule By Molecule Eberly College Of Science

Solutions Chapter 22 How Solutions Form Solution A Mixture That Appears The Same Throughout And Is Mixed At The Molecular Level 1 Solute Substance Ppt Download

Dissolving And Back Again American Chemical Society

Endothermic Vs Exothermic Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Worksheets Science Teaching Resources
Solubility And Molecular Structure

Let S Mention The Difference Between A Solution And A Heterogeneous Mixture A Solution Is A Combinat Chemical Science Solutions And Mixtures Materials Science

Dissolution Process An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Use This Lessonplan When Teaching Why Water Dissolves Sugar In Your Middleschool Science Classroom Middle School Chemistry Science Method Science Lessons

Aqueous Reaction Concentration Dissociation And Ionization Double Displacement Reactions Precipitation Gas Evolving Acid Base Neutralization Ionic Equation Ppt Download

How Do Aqueous Solutions Of Ionic Molecular Compounds Differ Study Com
Dissolving And Back Again American Chemical Society
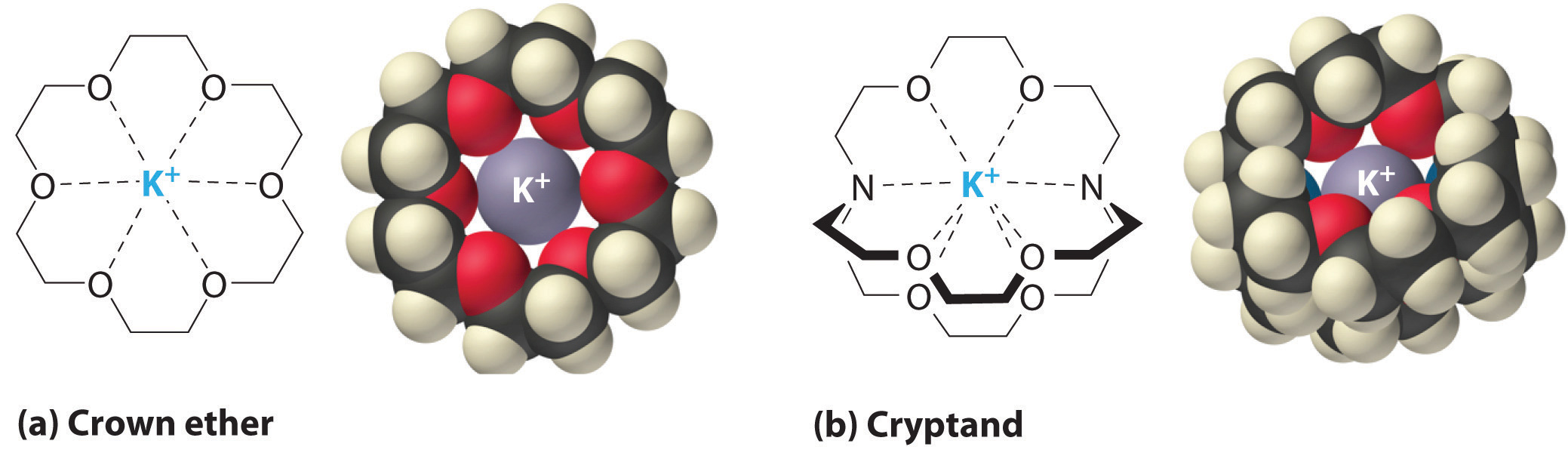
Solubility And Molecular Structure
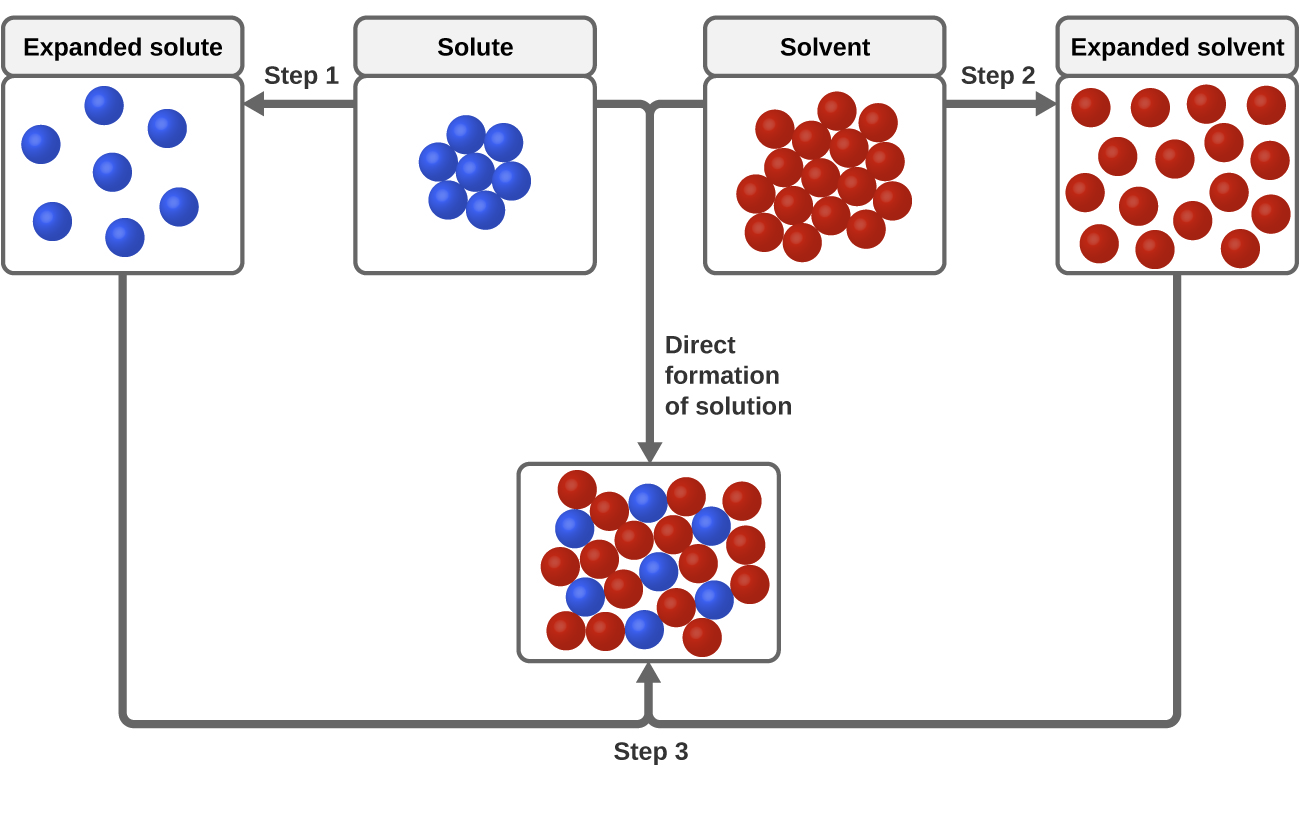
11 1 The Dissolution Process Chemistry

Properties Of Solutions Boundless Chemistry

Dissolving Process Chemistry For Non Majors

Water Molecules And Their Interaction With Salt U S Geological Survey
Comments
Post a Comment